异步调用
功能描述
背景
从 2.7.0 开始,Dubbo 的所有异步编程接口都基于 CompletableFuture
基于 NIO 的非阻塞实现的并行调用,客户端无需启动多线程即可完成对多个远程服务的并行调用,多线程的开销相对较小。
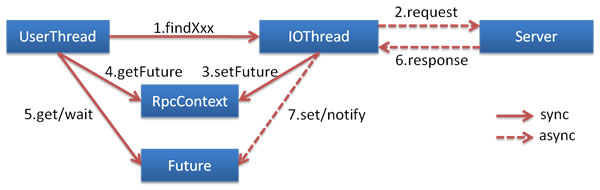
参考用例
https://github.com/apache/dubbo-samples/tree/master/dubbo-samples-async
使用场景
将用户请求内容发送到目标请求。当目标请求遇到高流量或需要长时间处理时,异步调用功能将允许立即将响应返回给用户,而目标请求在后台继续处理请求。当目标请求返回结果时,内容将被发送并显示给用户。
如何使用
带有 CompletableFuture 签名的接口
对于需要服务提供者提前定义 CompletableFuture 签名的服务,接口定义指南如下
提供者端的异步执行将阻塞业务从 Dubbo 的内部线程池切换到业务定义的线程,避免过度占用 Dubbo 线程池,并有助于避免不同服务之间的相互影响。异步执行等同于节省资源或提高 RPC 响应性能,因为如果业务执行需要阻塞,总会有一个线程负责执行。
提供者端的异步执行和消费者端的异步调用相互独立,两种配置的任何正交组合
- 消费者同步 - 提供者同步
- 消费者异步 - 提供者同步
- 消费者同步 - 提供者异步
- 消费者异步 - 提供者异步
定义 CompletableFuture 签名的接口
服务接口定义
public interface AsyncService {
CompletableFuture<String> sayHello(String name);
}
服务实现
public class AsyncServiceImpl implements AsyncService {
@Override
public CompletableFuture<String> sayHello(String name) {
return CompletableFuture. supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(name);
try {
Thread. sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "async response from provider.";
});
}
}
通过 return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(),业务执行已从 Dubbo 线程切换到业务线程,避免了 Dubbo 线程池的阻塞。
使用 AsyncContext
Dubbo 提供了一个类似于 Servlet 3.0 的异步接口 AsyncContext,它也可以在提供者端实现异步执行,而无需 CompletableFuture 签名接口。
服务接口定义
public interface AsyncService {
String sayHello(String name);
}
服务暴露,与普通服务完全相同
<bean id="asyncService" class="org.apache.dubbo.samples.governance.impl.AsyncServiceImpl"/>
<dubbo:service interface="org.apache.dubbo.samples.governance.api.AsyncService" ref="asyncService"/>
服务实现
public class AsyncServiceImpl implements AsyncService {
public String sayHello(String name) {
final AsyncContext asyncContext = RpcContext. startAsync();
new Thread(() -> {
// If you want to use the context, it must be executed in the first sentence
asyncContext.signalContextSwitch();
try {
Thread. sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// write back the response
asyncContext.write("Hello " + name + ", response from provider.");
}).start();
return null;
}
}
请注意,接口的返回类型是 CompletableFuture<String>。
XML 引用服务
<dubbo:reference id="asyncService" timeout="10000" interface="com.alibaba.dubbo.samples.async.api.AsyncService"/>
调用远程服务
// The call directly returns CompletableFuture
CompletableFuture<String> future = asyncService.sayHello("async call request");
// add callback
future. whenComplete((v, t) -> {
if (t != null) {
t. printStackTrace();
} else {
System.out.println("Response: " + v);
}
});
// earlier than the result output
System.out.println("Executed before response return.");
使用 RpcContext
在 consumer.xml 中配置
<dubbo:reference id="asyncService" interface="org.apache.dubbo.samples.governance.api.AsyncService">
<dubbo:method name="sayHello" async="true" />
</dubbo:reference>
调用代码
// this call returns null immediately
asyncService.sayHello("world");
// Get the Future reference of the call, when the result is returned, it will be notified and set to this Future
CompletableFuture<String> helloFuture = RpcContext.getServiceContext().getCompletableFuture();
// add callback for Future
helloFuture. whenComplete((retValue, exception) -> {
if (exception == null) {
System.out.println(retValue);
} else {
exception. printStackTrace();
}
});
或者,也可以通过调用来异步执行此操作
CompletableFuture<String> future = RpcContext.getServiceContext().asyncCall(
() -> {
asyncService.sayHello("oneway call request1");
}
);
future. get();
异步始终不等待返回,还可以设置是否等待消息发送
sent="true"等待消息发送,如果消息发送失败,将抛出异常。sent="false"不等待消息发送,将消息放入 IO 队列,立即返回。
<dubbo:method name="findFoo" async="true" sent="true" />
如果您只想异步执行并完全忽略返回值,可以配置 return="false" 以减少创建和管理 Future 对象的成本
<dubbo:method name="findFoo" async="true" return="false" />
